Zika Virus
Resources for preventing mosquito bites and protecting yourself from the harmful diseases they carry.
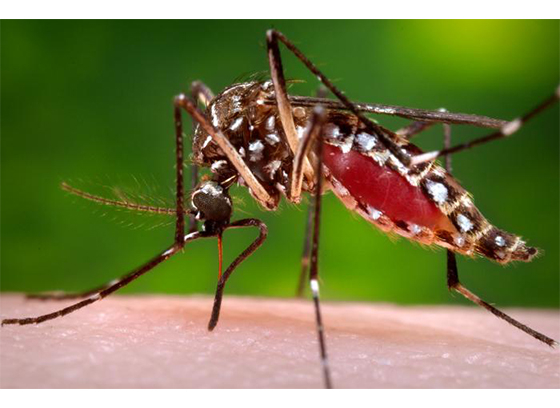
Zika virus disease (Zika) is a disease caused by the Zika virus, which is spread to people primarily through the bite of an infected Aedes species mosquito.
- The most common symptoms of Zika are fever, rash, joint pain, and conjunctivitis (red eyes).
- The illness is usually mild with symptoms lasting for several days to a week after being bitten by an infected mosquito. People usually don’t get sick enough to go to the hospital, and they very rarely die of Zika. For this reason, many people might not realize they have been infected.
- Zika virus infection during pregnancy can cause a serious birth defect called microcephaly, as well as other severe fetal brain defects.
- Once a person has been infected, he or she is likely to be protected from future infections.
- Currently, there is no vaccine to prevent or treatment for Zika virus infection.
Remember Zika is still a concern in many countries. Watch this video from the CDC to help you pack the essentials to prevent the risk of mosquito bites while staying in Zika areas.
There are local mosquito-borne Zika virus disease cases reported in US states, and many travel-associated cases. Visit the CDC website for current case numbers.
In the State of Maryland we have NO Locally Acquired Cases. Visit the Maryland Department of Health (MDH) Zika Virus Information page for state-wide guidance and information. A list of countries and territories with active Zika virus transmission can be found on the CDC website.
To Protect Yourself from Mosquito Bites
- Wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants.
- Stay in places with air conditioning and window and door screens to keep mosquitoes outside.
- Sleep under a mosquito bed net if you are overseas or outside and are not able to protect yourself from mosquito bites.
- Stay in places with air conditioning and window and door screens to keep mosquitoes outside.
To Protect Your Child from Mosquito Bites
- Do not use insect repellent on babies younger than 2 months old.
- Do not apply insect repellent onto a child’s hands, eyes, mouth, and cut or irritated skin.
- Adults: Spray insect repellent onto your hands and then apply to a child’s face.
- Cover crib, stroller, and baby carrier with mosquito netting.
- Dress your child in clothing that covers arms and legs.
- Do not use products containing oil of lemon eucalyptus or para-menthane-diol on children younger than 3 years old.
Treat Your Clothing and Gear
- Treat clothing and gear with permethrin or purchase permethrin-treated items.
- Treated clothing remains protective after multiple washings. See product information to learn how long the protection will last.
- If treating items yourself, follow the product instructions carefully.
- Do NOT use permethrin products directly on skin. They are intended to treat clothing.
(Information provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
Even if they do not feel sick, travelers returning to the United States from an area with Zika should take steps to prevent mosquito bites for 3 weeks so they do not spread Zika to mosquitoes that could spread the virus to other people.
- During the first week of infection, Zika virus can be found in the blood and passed from an infected person to another mosquito through mosquito bites. An infected mosquito can then spread the virus to other people.
- To help prevent others from getting sick, strictly follow steps to prevent mosquito bites during the first week of illness.
- Zika virus can be spread during sex by a man infected with Zika to his sex partners.
- We do not know how long the virus can stay in the semen of men who have had Zika, and how long the virus can be spread through sex.
- We do know that the virus can stay in semen longer than in blood.
- To help prevent spreading Zika from sex, you can use condoms, correctly from start to finish, every time you have sex. This includes vaginal, anal, and oral sex. Not having sex is the only way to be sure that someone does not get sexually transmitted Zika virus.
(Information provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)